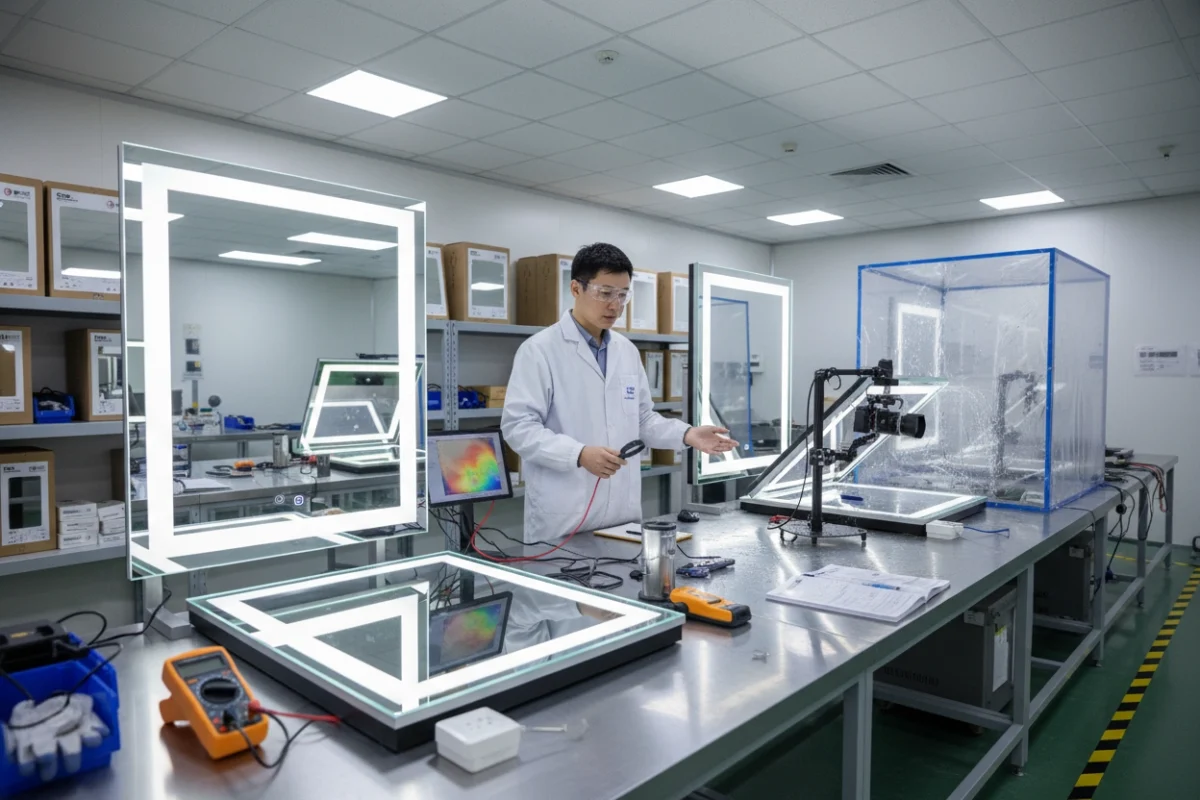
How to Produce LED Mirrors: A Complete Manufacturing Guide
LED mirrors have revolutionized modern bathroom design and functionality, combining traditional reflective surfaces with advanced lighting technology. This comprehensive guide explores the complete manufacturing process, from initial design to final quality control, providing insights into how these sophisticated products are created.
Understanding LED Mirror Technology
LED mirrors integrate Light Emitting Diode (LED) technology with high-quality mirror glass to create illuminated reflective surfaces. These products offer superior lighting for grooming tasks while consuming significantly less energy than traditional incandescent lighting solutions. The manufacturing process requires precision engineering, quality materials, and strict quality control measures to ensure safety and durability.
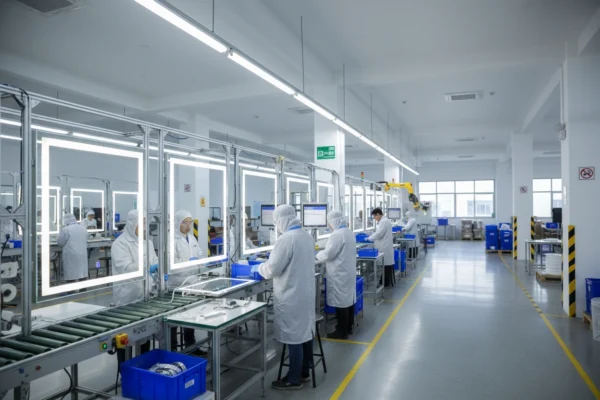

Essential Components and Materials
Core Components
The production of LED mirrors requires several key components that work together to create the final product:
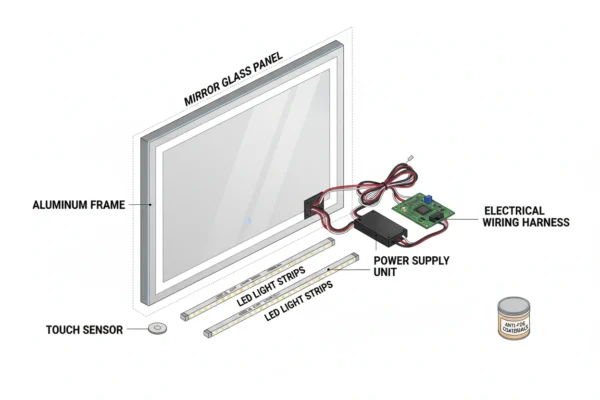
Mirror Glass: High-quality float glass serves as the foundation, typically 4-6mm thick with excellent reflectivity and clarity. The glass must be scratch-resistant and meet commercial-grade standards for durability.
LED Light Strips: Energy-efficient LED strips provide consistent illumination around the mirror perimeter. These strips must offer uniform brightness distribution and long operational life, typically rated for 50,000+ hours.
Power Supply Unit: Converts standard AC power to the low-voltage DC required by LED strips, incorporating safety features and energy efficiency standards.
Control Circuitry: Manages lighting functions including on/off switching, dimming capabilities, and smart features like touch controls or motion sensors.
Frame and Housing: Aluminum or high-grade plastic frames provide structural support and protection for electrical components while maintaining aesthetic appeal.
Electrical Wiring: High-quality wiring harnesses connect all electrical components safely and reliably, meeting electrical safety standards.
Manufacturing Process Overview
1. Design and Planning Phase
The manufacturing process begins with detailed design specifications that consider:
-
Mirror dimensions and shape requirements
-
LED placement and lighting distribution
-
Electrical component integration
-
Safety and regulatory compliance
-
Aesthetic design elements
2. Glass Processing and Preparation
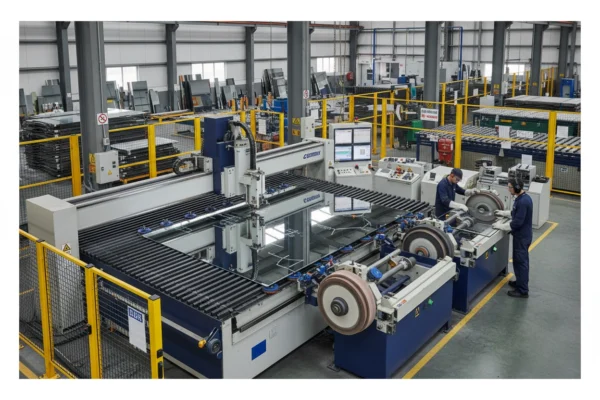

Glass Cutting: Precision machinery cuts float glass to exact specifications using diamond-tipped cutting tools. Computer-controlled systems ensure accuracy and minimize waste.
Edge Processing: Glass edges are polished and finished for safety and aesthetic appeal. This process removes sharp edges and creates smooth, professional-looking borders.
Surface Treatment: The mirror surface receives specialized coatings including:
-
Silver backing for reflectivity
-
Protective copper coating
-
Anti-corrosion paint layers
-
Optional anti-fog treatments
3. LED Strip Integration
Strip Selection: LED strips are chosen based on color temperature (typically 3000K-6500K), brightness output, and power consumption requirements.
Installation Process: LED strips are carefully positioned around the mirror perimeter or integrated into the frame structure. Proper spacing ensures uniform light distribution without visible hot spots.
Electrical Connections: All LED strips are connected to the control circuitry using waterproof connectors suitable for bathroom environments.
4. Frame Assembly and Integration
Frame Construction: Frames are manufactured from aluminum extrusions or molded plastics, providing channels for LED strips and electrical components.
Component Housing: Power supplies, control circuits, and wiring are securely housed within the frame structure, protected from moisture and physical damage.
Assembly Process: Mirror glass is mounted to the frame using appropriate adhesives and mechanical fasteners, ensuring long-term stability.
5. Electrical System Integration
Wiring Installation: All electrical components are connected according to detailed wiring schematics, ensuring proper functionality and safety.
Control System Setup: Touch sensors, dimmer controls, and smart features are integrated and calibrated for optimal performance.
Safety Features: Ground fault protection, overcurrent protection, and moisture barriers are implemented to meet electrical safety standards.
Quality Control and Testing
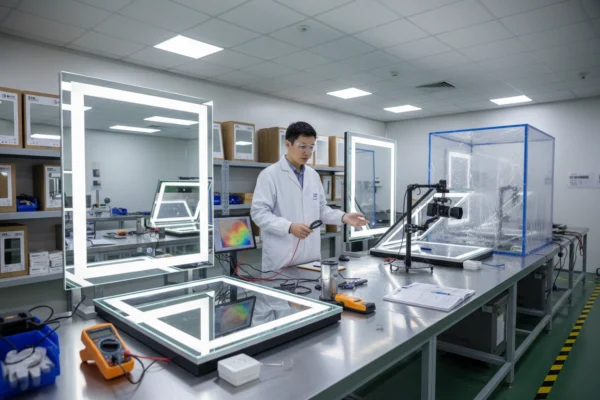

Comprehensive Testing Procedures
Electrical Safety Testing: All mirrors undergo rigorous electrical safety testing including:
-
Insulation resistance measurements
-
Ground continuity verification
-
Leak current testing
-
Overvoltage protection validation
Performance Testing: Functional testing ensures:
-
Uniform light distribution across the mirror surface
-
Proper dimming functionality
-
Touch control responsiveness
-
Anti-fog system effectiveness (if equipped)
Durability Testing: Long-term reliability testing includes:
-
Thermal cycling tests
-
Humidity exposure testing
-
Vibration and shock testing
-
Accelerated aging tests
Visual Inspection: Each mirror undergoes detailed visual inspection for:
-
Glass clarity and defects
-
LED alignment and uniformity
-
Frame finish quality
-
Overall aesthetic appearance
Compliance Standards
LED mirrors must meet various international standards including:
-
UL/ETL Certification: North American electrical safety standards
-
CE Marking: European conformity requirements
-
IP Rating: Ingress protection for moisture resistance
-
RoHS Compliance: Restriction of hazardous substances
-
Energy Star: Energy efficiency standards
Production Equipment and Machinery
Essential Manufacturing Equipment
Glass Cutting Systems: CNC-controlled glass cutting tables with diamond scribing wheels for precision cutting and minimal waste.
Edge Polishing Machines: Automated edge polishing equipment for consistent finish quality and worker safety.
LED Mounting Equipment: Specialized fixtures and jigs for accurate LED strip placement and alignment.
Testing Equipment:
-
Electrical safety analyzers
-
Photometric measurement systems
-
Environmental test chambers
-
Visual inspection stations
Assembly Tools: Pneumatic fastening systems, adhesive application equipment, and quality control measurement tools.
Packaging and Shipping
Protective Packaging
LED mirrors require specialized packaging to prevent damage during transportation:
-
Anti-scratch protective films
-
Shock-absorbing foam inserts
-
Moisture barrier materials
-
Sturdy corrugated boxes with impact protection
Quality Documentation
Each mirror includes:
-
Product specifications and certifications
-
Installation instructions
-
Warranty information
-
Safety guidelines and compliance documentation
Sustainability and Environmental Considerations
Eco-Friendly Manufacturing Practices
Modern LED mirror production incorporates sustainable practices:
-
Material Selection: Use of lead-free glass and RoHS-compliant components
-
Energy Efficiency: LED technology reduces operational energy consumption by 80% compared to incandescent lighting
-
Waste Reduction: Optimized cutting patterns minimize glass waste
-
Water Conservation: Closed-loop water systems for glass processing
-
Recycling Programs: End-of-life product recycling initiatives
Environmental Benefits
LED mirrors contribute to environmental sustainability through:
-
Reduced energy consumption during use
-
Longer product lifespan reducing replacement frequency
-
Mercury-free LED technology
-
Recyclable materials in construction
Cost Considerations and Production Economics
Manufacturing Cost Factors
-
Raw Materials: Glass, LED components, and electrical parts typically represent 40-50% of production costs
-
Labor: Assembly and quality control processes require skilled technicians
-
Equipment: Initial investment in specialized machinery and testing equipment
-
Compliance: Certification and testing costs for regulatory compliance
-
Packaging: Protective packaging materials and logistics
Production Efficiency
Optimizing production efficiency involves:
-
Automated assembly processes where possible
-
Streamlined quality control procedures
-
Efficient material handling systems
-
Continuous improvement in manufacturing processes
Future Trends and Innovations
Emerging Technologies
The LED mirror industry continues to evolve with:
-
Smart Mirror Integration: Incorporation of displays and IoT connectivity
-
Advanced Sensors: Motion detection and ambient light adjustment
-
Wireless Technology: Bluetooth connectivity and wireless charging capabilities
-
Sustainable Materials: Development of eco-friendly frame materials and coatings
Market Developments
Growing market demand drives innovation in:
-
Customization capabilities for unique designs
-
Improved energy efficiency standards
-
Enhanced durability and longevity
-
Integration with smart home systems
Conclusion
LED mirror production represents a sophisticated manufacturing process that combines traditional glassworking techniques with modern electronics and lighting technology. Success in this industry requires attention to detail, commitment to quality, and adherence to safety standards. As technology continues to advance and market demand grows, manufacturers must balance innovation with reliability to produce LED mirrors that meet consumer expectations for both functionality and durability.
The key to successful LED mirror production lies in understanding each component of the manufacturing process, from initial design through final quality control. By following established best practices and maintaining high standards throughout production, manufacturers can create products that provide years of reliable service while meeting all safety and performance requirements.

